🔋 The Future of Energy Storage: From Primitive Batteries to Solid-State and Beyond 🌍
Energy storage is the backbone of modern technology, enabling the functionality of everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. As we transition towards a more sustainable future, energy storage plays an even bigger role in renewable energy systems. The question is, how did we get to where we are today, and what does the future hold?
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the history of batteries, the game-changing innovations in solid-state battery technology, and what lies ahead for the future of energy storage.
The Dawn of Battery Technology ⚡
The history of energy storage stretches back millennia. One of the earliest known examples of energy storage devices is the Baghdad Battery, an ancient artifact discovered in Iraq that dates back to around 250 BCE. The purpose of this device remains a topic of debate, but it’s believed to have been used for electroplating or generating small amounts of electricity.
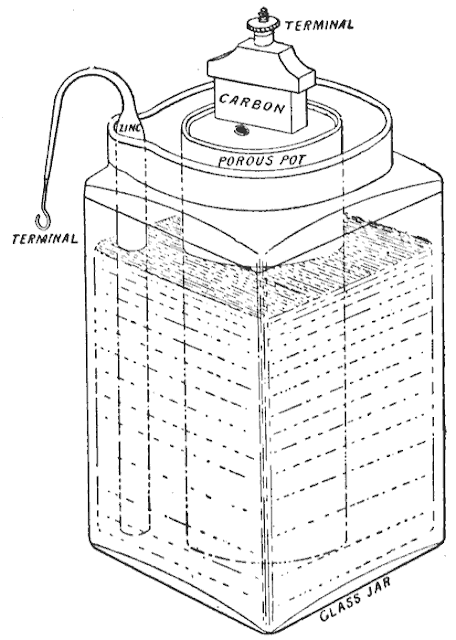
Fast forward to 1800, and we encounter the invention of the first true battery by Alessandro Volta, an Italian physicist. His Voltaic Pile marked the birth of modern battery technology. It consisted of alternating zinc and copper discs, separated by layers of cardboard soaked in saltwater. This invention paved the way for many of the electrical devices that would follow.
By the mid-19th century, more advanced batteries had begun to emerge:
- 1836: The Daniell Cell, which improved upon the Voltaic Pile and was used for telegraphs and doorbells.
- 1866: The Leclanché cell, which became the precursor to modern alkaline batteries.
- 1899: Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) batteries, the first rechargeable batteries, providing significant advancements in energy storage.
These innovations laid the foundation for the modern energy landscape, but the most profound changes were still to come.
The Lithium-Ion Battery Revolution 🔋
The 20th century saw the rise of lithium-ion batteries, the technology that has powered our modern world since its commercial debut in the 1990s. These batteries, capable of storing large amounts of energy in a lightweight, rechargeable format, revolutionized industries from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.
What makes lithium-ion batteries so effective? They offer a high energy density, which means they can store a significant amount of energy in a compact form. This made them essential for devices like smartphones and laptops, where space is limited but performance is paramount.
However, lithium-ion batteries are not without their limitations:
- Lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries degrade over time, leading to shorter usage periods and eventual replacement.
- Safety: They are prone to overheating and can, in rare cases, catch fire.
- Cost: The production of lithium-ion batteries is expensive due to the need for specific materials like cobalt and lithium.
These challenges have spurred scientists to explore alternative energy storage solutions, with solid-state batteries emerging as one of the most promising candidates.
Enter Solid-State Batteries: The Next Big Thing 🌍
Solid-state battery technology is poised to be the future of energy storage. The difference between solid-state batteries and traditional lithium-ion batteries lies in their electrolyte. Lithium-ion batteries use a liquid or gel electrolyte, while solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte. This seemingly simple change brings about several significant benefits.
Why Solid-State Batteries Are a Game-Changer:
- Higher Energy Density: Solid-state batteries can store more energy in a smaller, lighter form, which is particularly valuable for electric vehicles and portable electronics.
- Improved Safety: Without a flammable liquid electrolyte, solid-state batteries are much less likely to overheat or catch fire, making them a safer option.
- Faster Charging: Solid-state batteries can be charged more quickly than lithium-ion batteries, cutting down on waiting times and improving overall efficiency.
- Longer Lifespan: The solid electrolyte in these batteries is more stable and durable, leading to fewer charge cycles and a longer battery life.
Despite their promise, solid-state batteries face a few significant hurdles. The most pressing challenge is their cost. The materials and manufacturing processes required for solid-state batteries are expensive, and scaling production for widespread use is a complex task. However, with ongoing research and technological advancements, these obstacles are likely to be overcome in the near future.
Beyond Solid-State: What’s Next for Energy Storage? 🔮
While solid-state technology holds immense potential, other innovations in energy storage are also on the horizon. Let’s explore a few of the most exciting developments:
Flow Batteries: These batteries use liquid electrolytes that flow through a system to store energy. Flow batteries are especially suited for large-scale energy storage, such as renewable energy grids, because they can hold substantial amounts of energy for long periods.
Graphene-Based Batteries: Known for its strength and conductivity, graphene has the potential to revolutionize batteries by offering faster charging times, higher energy capacity, and longer lifespan.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity with water as a byproduct. This clean energy source could be key for powering vehicles and even entire buildings, providing a renewable solution for large-scale energy needs.
Quantum Batteries: Though still theoretical, quantum batteries are based on quantum mechanics and could offer extremely fast charging times and an unmatched energy capacity. This could be the next frontier of energy storage.
Implications for Renewable Energy 🌞
As the world shifts toward renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, energy storage will become even more critical. Renewable energy generation is intermittent, relying on the sun shining or the wind blowing. Batteries are needed to store excess energy generated during peak production times so that it can be used when generation is low.
Solid-state batteries, with their improved efficiency and safety, could become essential components of renewable energy grids. They could store energy more effectively and distribute it more reliably, allowing us to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and move toward a cleaner energy future.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Energy Storage 💡
From the ancient Baghdad Battery to today’s cutting-edge lithium-ion and solid-state technologies, the history of energy storage is a testament to human innovation. As we look ahead, solid-state batteries appear poised to revolutionize the field, offering safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting solutions for a world that increasingly relies on renewable energy.
But solid-state is just the beginning. With advancements in flow batteries, graphene-based systems, hydrogen fuel cells, and even quantum technologies, the future of energy storage is as exciting as ever.
As we continue to innovate, the possibilities for energy storage are vast, shaping not only the way we power our devices but the future of global energy infrastructure.
"Power up your devices with Duracell Coppertop AA Batteries—featuring Power Boost technology for extra-long life! Get a 24-count pack at an unbeatable value for reliable performance in every charge!"


























No comments:
Post a Comment